Gambling in India remains illegal, primarily under the Public Gambling Act, 1867, a colonial-era law that prohibits betting and gambling activities. However, there are significant complexities: states in India have the authority to regulate or prohibit gambling within their jurisdictions, leading to variations.
A study with 1514 Indian men showed 45.4% gambled in the past year, with lottery being the most frequent form (67.8%). Lifetime gambling prevalence was 49.9%. Gambling was correlated with rural residence, work-related problems, interpersonal violence, tobacco use, and alcohol use disorders (AUD), according to Bhatia et al’s 2019 research titled, “The Prevalence, Patterns, and Correlates of Gambling Behaviours in Men” published in the Asian Journal of Psychiatry.
In 2025, India’s Parliament passed the Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming Bill, which bans all online real-money games, whether based on skill or chance, across India. This ban comes amid concerns over addiction, financial scams, and national security risks, affecting the fast-growing online gaming market worth billions of dollars.
What are the effects of Gambling Addiction?
The effects of gambling addiction are financial difficulties and deteriorating mental health. This addiction strains personal relationships due to secrecy, lies, and economic stress, resulting in breakups or divorce.
- Financial Difficulties: Gambling addiction leads to significant money loss, resulting in debts, borrowing, or even bankruptcy. This economic strain can make it difficult to meet everyday expenses and long-term financial goals.
- Deteriorating Mental Health: The stress and guilt from compulsive gambling can increase anxiety, depression, and feelings of helplessness. Over time, these mental health issues can worsen, potentially leading to suicidal thoughts or behaviours.
- Strained Personal Relationships: Addicts frequently hide their gambling habits, leading to mistrust and frequent arguments with family and friends. The ongoing secrecy and lies erode the foundation of these relationships, sometimes leading to breakups or divorce.
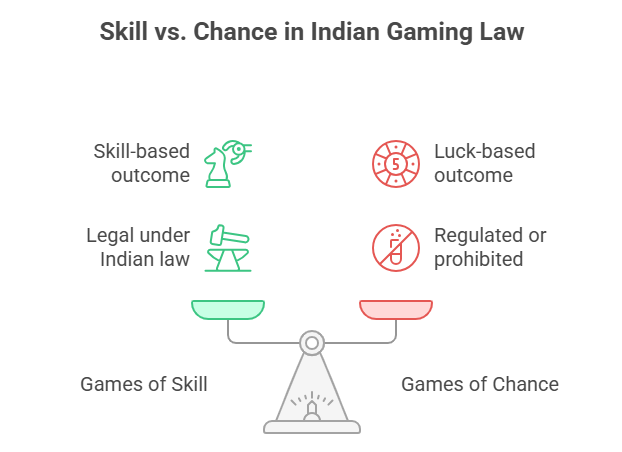
How Does Indian Law Differentiate Between Games of Skill and Games of Chance?
The Indian law differentiates games of skill and games of chance based on the predominance of skill or luck in determining the outcome. A game is classified as a game of skill if success predominantly depends on the player’s mental or physical skill, strategy, and decision-making, even if there is some element of chance. Conversely, games where the outcome relies mainly on luck or chance are classified as games of chance.
The Supreme Court of India has held that games like rummy and fantasy sports are games of skill because they require memorisation, strategy, and skilful play. In contrast, games such as lotteries and “Teen Patti” are games of chance. The key test used is whether skill predominates over chance in determining the result.
In essence, if skill is the dominant factor, the game is not gambling under Indian law; if chance is dominant, the game is considered gambling and is generally prohibited or regulated under gambling laws.
Which States Allow Skill-based Gambling or Betting in India?
The Indian states that currently allow skill-based gambling or betting are Sikkim, Nagaland, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Goa, Daman, and Diu.
Below are the states that allow skill-based gambling or betting in India.
- Sikkim: Legalises online casinos, sports betting, and skill-based games such as poker and rummy.
- Nagaland: Allows legal online skill-based games, including chess, poker, fantasy sports, and rummy, but prohibits games of chance.
- Chhattisgarh: Recently legalised land-based and online skill gaming with stakes under the Chhattisgarh Gambling (Prohibition) Act 2022.
- West Bengal: Allows skill-based online games, including poker, rummy, and fantasy sports.
- Tamil Nadu has a regulatory regime for online skill-based games, and the Madras High Court has ruled that skill-based games, such as poker and rummy, must be permitted despite some prohibitions in state law.
- Goa, Daman, and Diu: Allow regulated casino gambling, including skill games, under specific licensing laws.
Several other states, such as Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Assam, generally ban real-money games of skill and chance. At the same time, horse racing with betting is legal in states like Maharashtra, Telangana, and West Bengal under regulated conditions.
Which Indian States Ban Gambling Outright?
The Indian States that ban gambling outright include Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, and Assam.
- Tamil Nadu: Banned online gambling and games of chance like poker and rummy through the Tamil Nadu Prohibition of Online Gambling and Regulation of Online Games Act, 2022. This ban came partly as a response to gambling-related suicides and public harm concerns.
- Andhra Pradesh has prohibited online gambling and betting, enforcing strict laws to curb these activities entirely within the state.
- Telangana: Enforces stringent laws banning online gambling, blocking many sites and apps under the Telangana Gaming Act 1974. The state also regulates horse racing betting separately.
- Odisha has imposed bans on online betting platforms, particularly targeting harmful unlicensed gambling to protect consumers.
- Assam: Outright bans betting on fantasy sports and other gambling activities to regulate gaming behaviour and prevent financial loss.
These states have taken decisive steps to prohibit gambling activities, particularly online and money-based gambling, citing public health, addiction, and financial distress as key reasons for bans. Other states, such as Goa, Sikkim, and West Bengal, allow regulated forms of gambling or skill-based games, whereas the above states have strict prohibitions in place.
What penalties exist for illegal gambling under current Indian law?
The penalties that exist for illegal gambling under current Indian law include up to three years of imprisonment or a fine of up to 1 crore rupees, or both, for operating real money games. For advertising such illegal gambling activities, the punishment can be up to two years in prison or a fine of up to 50 lakh rupees. Repeat offenders face even harsher penalties, including imprisonment from three to five years and fines ranging from 1 crore to 2 crore rupees.
Violations related to unauthorised financial transactions linked to gambling also carry similar penalties. These offences are classified as cognisable and non-bailable, allowing police to arrest without a warrant and making bail difficult. Companies and their directors involved in these illegal gambling activities are also held accountable, except for independent directors who can prove due diligence. In some states, more stringent laws impose penalties of 3 to 7 years in prison and fines up to ₹5 lakh, with police empowered for warrantless search, seizure, and arrest in gambling cases.
What are the social and economic concerns influencing gambling legislation in India?
The social and economic concerns influencing gambling legislation in India are addiction and mental health, financial distress and fraud, regulatory challenges, exploitation of vulnerable populations, and the impact on social cohesion and family life.
These concerns are both societal and economic, driving the government’s cautious and protective approach to gambling laws.
- Addiction and Mental Health: Gambling addiction leads to significant mental health issues, including depression and suicidal tendencies. The government’s legislation aims to treat gamblers as victims of addiction rather than criminals, emphasising protection and rehabilitation.
- Financial Distress and Fraud: Problem gambling results in financial ruin, bankruptcy, and debt for individuals and families. It also contributes to fraud and illegal money transactions, prompting strict penalties on gambling operators and financial facilitators.
- Regulatory Challenges: Online gambling operates in a largely unregulated legal grey zone, complicating law enforcement and the application of consistent standards across states. Legislation aims to close these legal loopholes and extend regulation to both physical and digital gambling spaces.
- Exploitation of Vulnerable Groups: Gambling disproportionately affects socially and economically disadvantaged populations, youth, and other vulnerable groups, leading to social and educational failures as well as psychological distress. Regulations seek to shield these groups from exploitative gambling practices.
- Social Cohesion and Family Impact: Gambling issues disrupt family relationships, increase social stigma, and burden social and health services. The laws reflect the need to maintain social harmony by minimising the social costs of gambling-related harms.
Social and economic concerns around gambling in India have led to legislation focused on protecting individuals and society from the harms of unregulated gambling while encouraging safe, innovative digital gaming alternatives. This balanced approach aims to support economic growth without compromising social welfare.
Is cricket betting legal in India?
No, cricket betting is not legal in India except in certain states where it is specifically allowed. Most forms of betting and gambling, including cricket betting, are prohibited by the Public Gambling Act of 1867 and various state laws. However, some states like Sikkim and Nagaland have regulated certain forms of betting. Online cricket betting operates in a legal grey area with regulatory uncertainty. It is considered illegal under current laws, but discussions about legalising and regulating sports betting, including cricket, are ongoing in India.
How is Gambling Linked to Issues Like Addiction, Financial Risks, and National Security?
Gambling is linked to addiction through compulsive behaviours that lead individuals to repeatedly gamble despite harmful consequences, resulting in mental health issues like depression and increased suicide risk.
Financial risks are significant as gambling drains personal and community resources, causes bankruptcy, and fosters economic instability. On a broader scale, gambling can threaten national security by weakening economies, reducing consumer spending and economic productivity, and facilitating money laundering and financing of terrorism, which compromises financial systems and governmental stability.
These intertwined harms make gambling a critical social and economic issue with far-reaching consequences beyond individual health, affecting national economies and security frameworks.





