A mental health disorder can be classified as a mental illness or a psychiatric disorder, which significantly affects an individual’s emotions and behavior. Individuals with mental disorders may feel anxious or empty, with trouble sleeping or eating. They are usually associated with impairment or distress, which affects their functioning.
Mental health disorders are categorised into mood, anxiety, psychotic, neurodevelopmental, addictive, and trauma-related disorders. This psychiatric illness has a debilitating impact on a person’s life. It can impact their daily functioning, relationships, physical health, and overall quality of life. The early signs of mental disorders can be observed by the changes in a person’s thoughts or feelings. For example, the early onset of psychological sickness can be observed in a person due to changing mood, social withdrawal, excessive fear, or use of substances.
Mental health disorders are caused by a mixture of factors. This may include biological factors (genetics, brain chemistry, or injury), physiological factors (trauma, stress, personality, or coping skills), and social factors (relationships, environment, or culture). It is thereby important to tackle the issue before it gets out of hand. It can be achieved by building good resilience and promoting good physical health. Additionally, having a good social system with a supportive environment can help you achieve the best results. However, if there are some initial signs of mental illness, it is a good choice to contact an expert.
What is Mental Health Disorder?
A mental health disorder can be classified as a wide range of mental health conditions that affect an individual’s behavior, mood, or thinking. These mental disorders severely affect the daily life and functioning of an individual. Good mental health allows individuals to tackle life events one step at a time and work productively.
Mental health disorders are very common, with 1 in 7 people around the world living with a mental disorder, as per the World Health Organisation (WHO). Another study by the WHO claims that more than 1 million people are suffering from mental illnesses like anxiety, depression, etc. The estimated loss alone due to anxiety and depression is roughly US$1 trillion per year in lost productivity globally. In India, 10.6% of adults suffer from mental disorders as per the National Health Survey by NIMHANS.
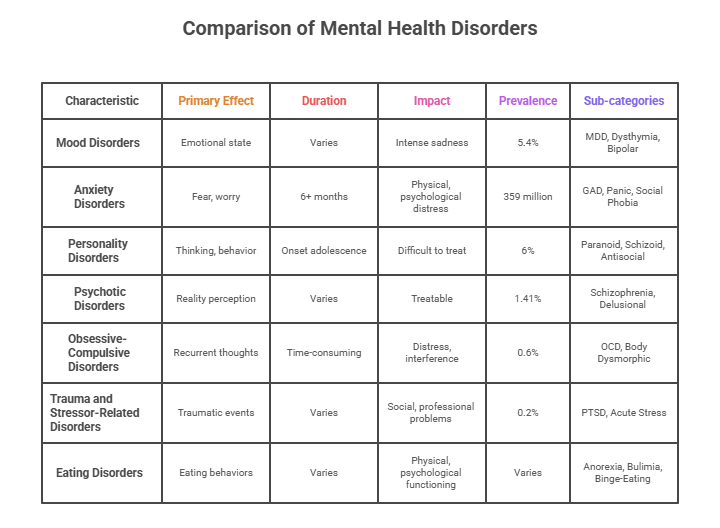
What are the main categories of mental health disorders?
The main categories of mental health disorders are mood disorders, anxiety disorders, personality disorders, psychotic disorders, obsessive-compulsive and related disorders, trauma and stressor-related disorders, and eating disorders. Let’s look at them in detail below.
Mood Disorders
Mood disorders are mental health conditions that have a primary effect on the emotional state of an individual. This mental illness causes intense sadness or anger, affecting them individually or their standing in society. The prevalence of mood disorders is 5.4% with its prevalence ranging from 0.8% to 9.6% across countries.
Some of the sub-categories of mood disorders include
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
- Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia)
- Bipolar I Disorder
- Bipolar II Disorder
- Cyclothymic Disorder
- Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
- Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a common mental health illness that causes fear, worry, or related behavioral disturbances. The disorders can last between 6 months and more if not treated. They cause severe physical and psychological distress, affecting the individual’s life. Around 359 million people are living with anxiety, as per a report by the WHO. In India, a staggering 44.9 million people suffer from anxiety disorders.
Some of the sub-categories of Anxiety disorders include
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Panic Disorder
- Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia)
- Agoraphobia
- Separation Anxiety Disorder
Personality Disorders
Personality disorders follow a disruptive pattern of thinking, behavior, and mood. Individuals with this disorder don’t understand or relate to the world around them. They usually don’t realize that their thoughts and behaviors are problematic. The mental illness usually starts at the onset of adolescence or early adulthood. Its complexity and rigidity of its patterns make it a very difficult mental health issue to treat. It is estimated that around 6% of the world’s population suffers from personality disorders.
Some of the sub-categories of Personality disorders include
- Paranoid Personality Disorder
- Schizoid Personality Disorder
- Schizotypal Personality Disorder
- Antisocial Personality Disorder
- Borderline Personality Disorder
- Histrionic Personality Disorder
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder
- Avoidant Personality Disorder
- Dependent Personality Disorder
Psychotic Disorders
Psychotic disorders or psychosis are conditions where a person finds it difficult to distinguish between what is real and what is not. It can be caused by several mental or physical conditions and is usually treatable with medication or other techniques. In fact, according to a study in 12 states of India, 1.41% of people showed signs of psychotic disorders, with a current prevalence of 0.42%.
Some of the sub-categories of Psychotic disorders include
- Schizophrenia
- Schizoaffective Disorder
- Brief Psychotic Disorder
- Delusional Disorder
- Schizophreniform Disorder
- Substance-Induced Psychotic Disorder
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is characterized by the presence of recurrent or persistent thoughts that are unwanted. They create a type of compulsion and cause time-consuming symptoms, which are marked by distress or interference with daily activities. A study from India stated that OCD had a lifetime prevalence of 0.6%. The rate in Europe and North America was between 2% to 3%.
Some of the sub-categories of Obsessive-Compulsive disorders include
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- Hoarding Disorder
- Trichotillomania (Hair-Pulling Disorder)
- Excoriation (Skin-Picking) Disorder
- Substance-Induced Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.
Trauma and Stressor-Related Disorders
Trauma and stressor-related disorders occur in response to or exposure to traumatic or stressful events. They involve a number of symptoms, including intrusive memories or reminders that alter the mood and arousal of the individual. The disorder makes it difficult to connect with others, leading to social and professional problems. The relevance of PTSD in India is 0.2%, which is lower than the global average. However, rates can be higher for disaster survivors or accident victims.
Some of the sub-categories of the disorders include
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Acute Stress Disorder
- Adjustment Disorders
- Reactive Attachment Disorder
- Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder
Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are severe problems associated with eating behaviors, which usually lead to distress and despair. The eating disorder impacts the physical and psychological functioning of the individual. In some cases, this food addiction can damage internal organs or cause psychological sickness.
Some of the sub-categories of the Eating disorders include
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Bulimia Nervosa
- Binge-Eating Disorder
- Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID)
- Pica
- Rumination Disorder
What is the impact of mental health disorder?
A mental health disorder extends far beyond an individual’s emotional state and influences every facet of the individual’s life. Physically, mental illness can cause serious medical conditions, like heart disease, stroke, or diabetes. Emotionally, individuals may suffer from extreme mood swings, hopelessness, or distress.
Relationships can have a severe impact due to mental health problems. This can be due to symptoms like volatile moods, irritability, or withdrawal fracturing bonds with friends and family. Socially, it can lead to discrimination and stigma about the condition. Professionally, it can diminish productivity, which will ultimately lead to unemployment, causing financial distress.
What are the early warning signs of mental health disorder?
Mental health awareness is vital to help the public identify potential mental health conditions and reduce stigma in society. It is therefore important to detect these issues at the start before they turn out to be a full-term illness. Early signs of mental illness can be categorized by their thoughts, behavior, and physical well-being.
The early signs in the categories include
Changes in Thoughts and Feelings
- Intense sadness or irritability
- Rapid mood swings
- Excessive fear or anxiety
- Loss of interest
Changes in Behavior
- Social withdrawal from friends and family
- Change in eating habits
- Changes in sleeping patterns
- Increased use of substances
- Self-harming behaviors
- Increased anger or aggressive behavior
Changes in Physical Well-Being
- Extreme fatigue or energy
- Persistent headaches
What are the first signs of a mental health issue?
The initial signs of mental health issues are changes in the thinking patterns or behavior, showing noticeable distress or changes in lifestyle. This shows a diminished capacity for pleasure or not being themselves for long periods, mostly over two weeks. If these changes are present, then it shows a significant deviation from the person’s baseline. This acts as a critical indicator of the development of psychological sickness.
How do I know if someone is struggling with a mental health disorder?
Identifying if someone is struggling with health problems can be done by closely observing their behaviors. An individual with a sudden change in behavior affecting their social and professional life responsibilities needs to be checked. Additionally, check whether they have low energy or show signs of risky behaviors. Apart from this, check whether their emotional response is disproportionate to the situation, suggesting a regulatory issue that is common with mental illnesses..
When should I consult a mental health professional?
The right time to consult a professional is when the symptoms cause significant distress or impairment in one’s life for over two weeks. Help may be needed quickly if there are signs of self-harm, suicide, or uncontrollable panic attacks.
What are the causes of mental health disorders?
The main cause of mental health is an interplay between biological, psychological, and environmental factors, as discussed in the Biopsychosocial Model. Let’s discuss the causes below.
Biological Causes
The biological causes affect the physical body of the individual. The main contributing factors to this include genetics, brain structure, and brain infections.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones influence the bodily functions and brain activity, helping in the development of the brain. Any changes to the hormonal activity, like in stress, thyroid hormones can affect the mental health of an individual.
Psychological Causes
The psychological cause relates to the individual’s thoughts, emotions, and coping skills. It may be caused by psychological trauma, personality traits, and any negative habits or thoughts.
Social Causes
The social causes may involve the person’s surroundings, relationships, or life experiences.
What are the prevention of mental health disorders?
Mental health disorder prevention aims to identify risk factors and strengthen positive factors for individuals, families, and communities. The importance of mental health disorders prevention can be seen in the WHO’s projection of investing in treatment for depression and anxiety. As per the report, investing in mental health treatment leads to a fourfold return on every dollar invested.
Prevention strategies need to be implemented across the entire population, risk groups, or individuals showing early symptoms. This can be done by
- Promoting Mental Health Awareness
- Building Strong Social Connections
- Managing Stress





